

This R package offers a fast, standardized and reproducible workflow for data from cardiopulmonary exercise testing. It offers tools for data import, processing, summary and visualization.
Measuring gas exchange during physical exercise is a common procedure in sports science and medicine. It allows to assess the functional limit of the cardiovascular system, evaluate the success of training interventions, and diagnose cardio-respiratory diseases. The measuring devices of cardiopulmonary exercise testing — so-called metabolic carts — output their data in different formats. Moreover, measured breath-by-breath data is noisy and requires post-processing. This package standardizes the import and processing of raw data from different metabolic carts.
Install spiro from CRAN:
install.packages("spiro")Install the current development version of spiro from
GitHub:
if (!require(remotes)) install.packages("remotes")
remotes::install_github("ropensci/spiro")Main functions:
spiro() to automatically import and process raw
data from cardiopulmonary exercise testing.spiro_summary() for a summary of cardiopulmonary
parameters (e.g., relative oxygen uptake, respiratory quotient, heart
rate, …) for each load step.spiro_max() to calculate maximum parameter values
(e.g., VO2max).spiro_plot() to visualize the data as a modifiable
Wassermann 9-Panel Plot.Further functionality:
The following metabolic carts are currently supported by
spiro:
Support for further metabolic carts is planned for future releases.
library(spiro)
# get data path for example
file <- spiro_example("zan_gxt")
# import and process the raw data
gxt_data <- spiro(file)
# summary of parameters by load step
spiro_summary(gxt_data)
#> for pre-measures, interval was set to length of measures (60 seconds)
#> step_number duration load VO2 VCO2 VE HR PetO2 PetCO2 VO2_rel
#> 1 0 60 0.0 500.19 411.74 13.03 NA NA NA 7.58
#> 2 1 300 2.0 1860.92 1585.75 39.87 NA NA NA 28.20
#> 3 2 300 2.4 2097.82 1805.27 44.63 NA NA NA 31.79
#> 4 3 300 2.8 2413.01 2122.17 52.63 NA NA NA 36.56
#> 5 4 300 3.2 2710.68 2319.93 57.19 NA NA NA 41.07
#> 6 5 300 3.6 3048.75 2684.87 67.45 NA NA NA 46.19
#> 7 6 300 4.0 3404.02 3026.70 75.91 NA NA NA 51.58
#> 8 7 300 4.4 3724.37 3383.64 88.36 NA NA NA 56.43
#> 9 8 300 4.8 4223.82 3993.55 106.44 NA NA NA 64.00
#> 10 9 300 5.2 4573.91 4488.36 127.54 NA NA NA 69.30
#> RE RER CHO FO
#> 1 NA 0.82 0.27 0.15
#> 2 234.97 0.85 1.27 0.46
#> 3 220.73 0.86 1.51 0.49
#> 4 217.62 0.88 1.95 0.48
#> 5 213.91 0.86 1.89 0.65
#> 6 213.86 0.88 2.47 0.60
#> 7 214.90 0.89 2.90 0.62
#> 8 213.75 0.91 3.50 0.56
#> 9 222.21 0.95 4.68 0.37
#> 10 222.12 0.98 5.82 0.12
# maximum values
spiro_max(gxt_data)
#> VO2 VCO2 VE VO2_rel RER HR
#> 1 4732.28 4640.75 129.62 71.7 0.99 NA
# Wassermann 9-Panel Plot
spiro_plot(gxt_data)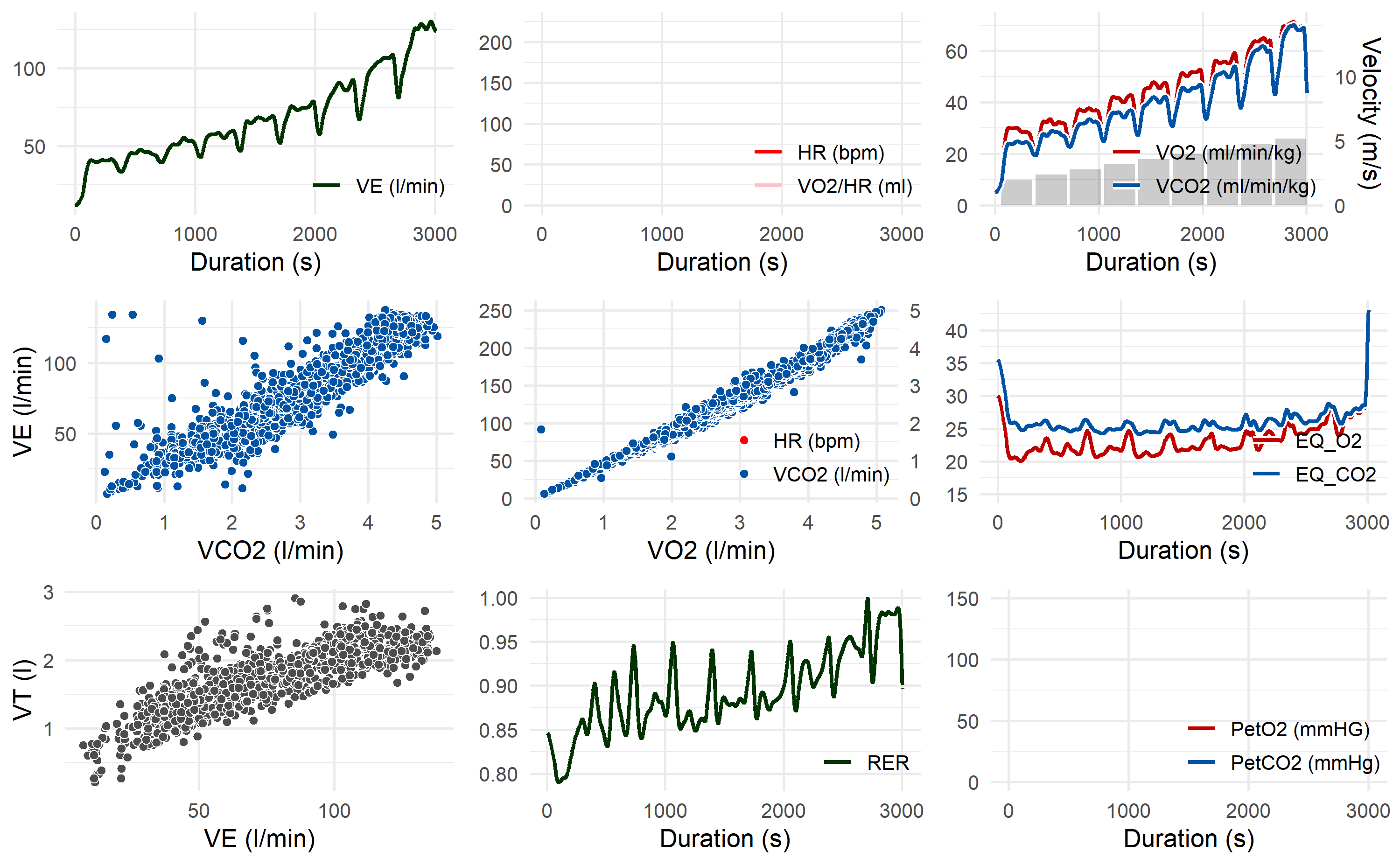
citation("spiro")To cite spiro in publications use:
Simon Nolte (2023). spiro: An R package for analyzing data from
cardiopulmonary exercise testing. Journal of Open Source Software,
8(81), 5089, https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.05089
A BibTeX entry for LaTeX users is
@Article{,
title = {spiro: An R package for analyzing data from cardiopulmonary exercise testing},
author = {Simon Nolte},
year = {2023},
volume = {8},
number = {81},
pages = {5089},
journal = {Journal of Open Source Software},
url = {https://joss.theoj.org/papers/10.21105/joss.05089},
doi = {10.21105/joss.05089},
}The whippr package offers a different approach to working with data from cardiopulmonary exercise testing. It additionally offers functions for analyzing VO2 kinetics.
The following persons contributed to this package by providing raw data files, reviewing code and/or suggesting features: Daniel Appelhans, Michael Beaven, James Hunter, Virgile Lecoultre, Sebastian Mühlenhoff, Manuel Ramon, Anton Schiffer, Yannick Schwarz, Adrian Swoboda, Andreas Wagner.
If you consider contributing to this package, read the CONTRIBUTING.md. Please note that this package is released with a Contributor Code of Conduct. By contributing to this project, you agree to abide by its terms.