The package treenomial is an application of polynomials that uniquely describe trees. It provides tools for tree analysis and comparison based on polynomials. The core functions are:
treeToPoly(): convert rooted
unlabeled binary trees to tree distinguishing polynomials described with
coefficient matrices
polyToDistMat(): construct a
distance matrix from multiple coefficient matrices using a distance
measure
For the mathematical description of the tree defining polynomial see:
Liu, Pengyu. “A tree distinguishing polynomial.” arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.03332 (2019).
To install using CRAN:
install.packages("treenomial")For the development version:
library(devtools)
install_github("mattgou1d/treenomial")Consider a three tip tree:
library(ape)
library(treenomial)
threeTipTree <- rtree(3, rooted = T)
plot.phylo(threeTipTree, use.edge.length = F, show.tip.label = F, direction = "downwards")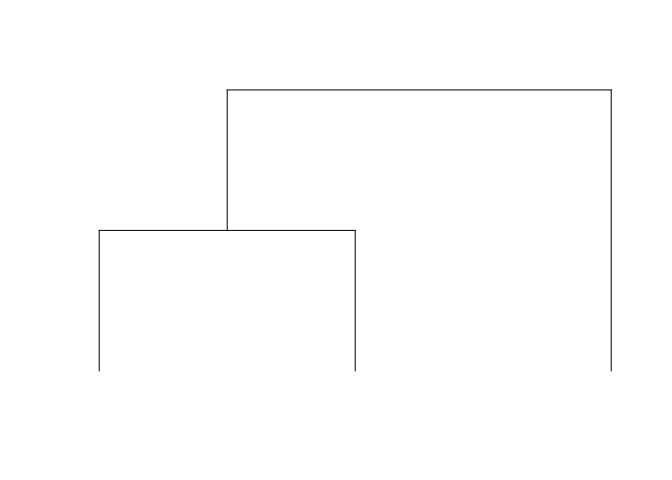
It’s polynomial is x^3+xy+y which can equivalently be described with a coefficient matrix where the element in the ith row, jth column represents the y^(i-1) * x^(j-1) coefficient:
treeToPoly(threeTipTree, varLabels = T)
#> x^0 x^1 x^2 x^3
#> y^0 0 0 0 1
#> y^1 1 1 0 0
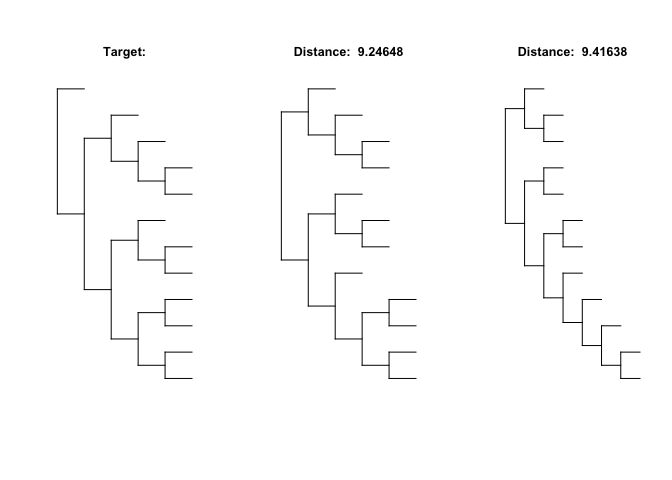
#> y^2 0 0 0 0Using the coefficients of the polynomials, distances between trees can be compared, below the two closest trees to a random target tree are found from a random sample:
# random 12 tip target tree
target <- rtree(12)
# random sample of 100 trees
sample <- rmtree(100,12)
minInfo <- plotExtremeTrees(target,sample, n = 2, comparison = "min", type = "d")